Mesh Wrap: A Free Terrain Wrapping Addon for Blender.
by Jettelly
Published |
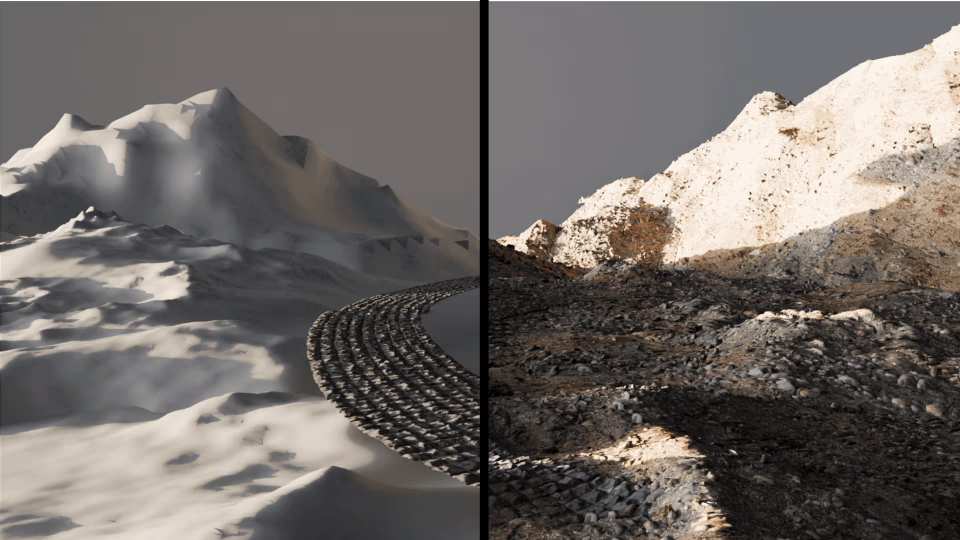
Working with scanned terrain, bricks, or surface fragments in Blender usually means stacking modifiers. Shrinkwrap, lattice adjustments, manual cleanup and duplicated helpers.
Mesh Wrap, a free Blender add-on by KIRI Engine, approaches the same problem from a better angle: wrapping terrain and scan-based meshes onto surfaces with fewer objects, fewer modifier stacks, and more control.
The addon is designed specifically around terrain and surface scans, not generic solid meshes, and that design choice shows throughout the workflow.
What Mesh Wrap Actually Does
Mesh Wrap lets you project one or many meshes onto a target surface using a ray-based wrapping system. Instead of relying on multiple modifiers, the add-on handles wrapping, displacement, boundary cleanup, and optional decimation inside a single tool.
There are two main workflows:
- Planar Wrap for wrapping a single object onto a surface
- Scatter Wrap for distributing and wrapping multiple meshes across terrain
Both are built around the same idea: rays are cast from the source mesh toward the target surface. If the rays hit, the mesh wraps. If they don't, the add-on tells you immediately.
This makes orientation, origin, and direction critical, which is why Mesh Wrap includes dedicated preparation tools instead of assuming "perfect" input geometry.
Mesh Preparation Is Not Optional (And That’s a Good Thing)
One of the most useful parts of the addon is that it forces you to think about mesh setup.
The documentation says that:
- The addon works best with open, non-manifold scan meshes
- Solid or fully closed meshes tend to produce unwanted results
- Mesh origin and rotation directly affect wrapping accuracy
To handle that, Mesh Wrap includes quick tools to:
- Auto-align meshes to world axes
- Rotate meshes in fixed 90-degree steps if alignment is off
- Set mesh origins to top, bottom, or midpoint along an axis
This is because wrapping scanned data is geometry-sensitive, and the add-on gives you tools to deal with it.
Planar Wrap: Controlled Projection
Planar Wrap is the simplest mode, but it already shows where Mesh Wrap differs from typical Shrinkwrap workflows.
Key points::
- Wrapping direction is explicit. You choose where rays are fired from.
- If the rays miss the surface, the add-on shows a warning state instead of silently failing.
- Displacement strength controls how much original surface detail is preserved.
- Sub-origin handling lets you decide whether concave details should push into the surface or snap cleanly.
Boundary handling is also more deliberate than usual. Floating edges can be snapped back to the surface with adjustable falloff, and overlapping geometry can either be removed or blended, depending on the use case.
This makes Planar Wrap especially useful for:
- Cliff faces
- Terrain decals
- Modular surface fragments
- Scan-based environment dressing
Scatter Wrap: Terrain Dressing Without Manual Placement
Scatter Wrap turns a surface into a scatter host and projects multiple meshes or entire collections onto it.
The add-on integrates cleanup directly into the process:
The add-on integrates cleanup directly into the process:
- Optional decimation for high-poly scan assets
- Grid, density, or amount-based scattering
- Poisson disk distribution to reduce overlaps
- Border masking to keep edges clean
Alignment can be planar or normal-based, which matters a lot on curved terrain. For uneven surfaces, normal alignment avoids the “floating card” look common in simpler scatter setups.
There are also preview modes that let you tweak density and seed values using lightweight point previews before committing to full geometry, which helps keep iteration fast on heavy scenes.
Cleanup Is Built In
Wrapping scanned meshes almost always creates edge cases:
- Overlapping geometry
- Faces stretched beyond reasonable limits
- Points that fail to hit the surface
Mesh Wrap exposes these problems. You can:
- Remove or preserve overlapping geometry
- Recover removed points using distance-based masking
- Remove stretched faces with adjustable thresholds
- Smooth base surface normals (non-destructively) to reduce artifacts
Performance
The documentation doesn’t oversell performance. KIRI Engine explicitly recommends:
- Using decimation when scattering scan assets
- Increasing scale before density to control poly counts
- Expecting very high polygon counts if you’re not careful
Mesh Wrap doesn’t magically optimize heavy scans. But it gives you tools to manage them.
🎥 The creators of the add-on also shared a 20+ minute tutorial walking through the tool’s features.
About the Download
Mesh Wrap is free, but downloading it from KIRI Engine’s site currently requires creating a KIRI Engine account.
This is worth mentioning clearly:
- The addon itself is free
- The account requirement exists because it’s part of KIRI Engine’s ecosystem
- Users are encouraged (but not required) to support the project via the KIRI Engine app
The add-on is also expected to appear on Superhive once approved.
Who This Addon Is For
Mesh Wrap makes the most sense if you:
- Work with photogrammetry or scanned terrain
- Build environment art with lots of surface dressing
- Want fewer helper objects and cleaner modifier stacks
- Prefer tools that expose constraints instead of hiding them
If you’re looking for a generic deformation tool for arbitrary meshes, this is probably not the right fit. The add-on is designed around terrain and surface-scan workflows.
Similar and Useful Tools
- Simply Wrap Pro: A Blender addon that lets you quickly wrap a mesh around another surface by drawing guide strokes. It automatically detects face orientation and generates a wrap mesh around characters, props or environment pieces.
Differences: Simply Wrap Pro focuses on fast interactive wrapping with drawn guides. Mesh Wrap by KIRI Engine may use a more automated projection approach tied to KIRI’s ecosystem, Simply Wrap Pro puts more user control into the wrapping shape via curve/guide drawing.
- Wrap Gen: A Blender generator that wraps custom geometry (ropes, ties, straps) around target meshes with detailed control over curves, offsets, randomisation and self-collision detection.
Differences: Wrap Gen is stronger for curved wraps and patterned geometry (like straps, cables or repetitive elements) rather than generic mesh projection. Mesh Wrap is broader and can be used for terrain/complex surface conformance, while Wrap Gen excels at controlled curve-driven wraps.
✨ Mesh Wrap v1.0.0 is now available on KIRI's Website.
📘 Interested in creating your own Tools and Shaders? Check out the Godot Shaders & Blender Tools Bundle, which includes: Blender Tool Development Fundamentals and The Godot Shaders Bible.
📘 Interested in creating your own Tools and Shaders? Check out the Godot Shaders & Blender Tools Bundle, which includes: Blender Tool Development Fundamentals and The Godot Shaders Bible.
Our best-selling indie Bundle: Godot shaders + Blender tools ✨ https://t.co/zSlHDCuGVC#b3d #GodotEngine #3DCG pic.twitter.com/sjdYxXjKUB
— The Unity Shaders Bible (@ushadersbible) November 16, 2025


.png)
